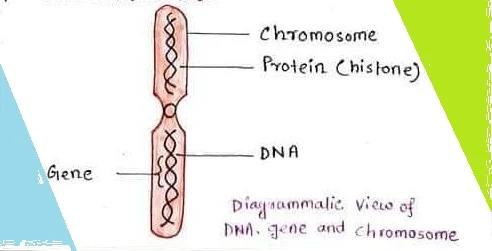
Genes are preset on chromosomes in a line, so chromosomes are the heredity vehicles that are passed on from parent cell to daughter cell and from parents to offspring. The chromosomes are contained within the nucleus of the cell and are formed of basic proteins histones and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
A gene is a short segment of a DNA chromosome. Each type of organism has a specific number of chromosomes on the individual from its genotype or genetic composition. The external features, appearance, morphology, anatomy, and behavior of an organism make its phenotype. The phenotype of an individual is the net result of interaction between genotype and environment.
Heredity and Variation
Genetics is a branch of biology that deals with as well as variation of characters from parents to offspring. The term genetics was first used by W. Bateson in 1905. Inheritance is the process by which characters are passed on from parents to progeny and is the basis of heredity.
Heredity
The term heredity may be defined as the transmission of genetically based characteristics from parents to offspring or the genetic constitution of an individual.
Like begets Like- It means that young ones look like their parents.
Cats produce to cats and not dogs.
A mango seed germinates into a mango tree.
Humans give birth only to humans and not apes.
Even the curd bacteria that grow in milk undergo hundreds of generations each day and continue to produce the same type of bacteria and not of any different type.
Like begets like and yet there are variations.
All Organisms whether animals, plants, or microorganisms, produce their own kind through reproduction. But the offspring are never identical to their parents, some difference, however small it may be, is found in them. Some may resemble more with the father while others may be more mother-like. These dissimilarities between brothers and sisters and between parents and offspring are called variations.
Inheritance:- Inheritance is the process by which genetic information is passed on from parent to child. This is why members of the same family tend to have similar characteristics.
Inheritance ( Genetic information)
Parents ----------------------> Offspring / Child
Heredity ( Features, Traits, Behaviour )
Character:- Any inheritable feature of an organism is a character. Exp. Color of the human eye.
Traits:- The alternative forms of a character are called traits. Exp. People with brown eyes.
Inheritance in Humans
We inherit thousands of characters from our parents (father and mother) who in turn inherited them from their parents. Thus the family members brothers, sisters, and casinos tend to resemble one another.
Difference Between Character and Traits
Character
(i) Color of eyes
(ii) Hair shape
(iii) Eyebrows
(iv) Hair on the middle joint of fingers
(v) Colour vision
(vi) Tongue rolling
(vii) Hand use
(viii) Skin color
(ix) Ear lobe
(x) Rh blood group.
Traits
(i) Brown or blue
(ii) curly or straight
(iii) Heavy, bushy or thin
(iv) Growth or no growth
(v) Normal or red-green color blindness
(vi) Rolling of the tongue into a U-shaped when extended out from the mouth or no-rolling.
(vii) Right-handedness or left-handedness
(viii) Albinism (total absence of pigment in the skin) or normal (light or dark) pigment.
(ix) Free or attached
(x) Rh- Rh-positive or Rh-negative.
Chromosomes The Carrier of Heredity
The Chromosome number is constant for the individuals of a species, and each body cell of that species has the same number of chromosomes. Humans have 46 chromosomes.
Chromosome numbers of some other common animals and plants are as follows.
Ascaris = 2
Humans = 46
Onion = 16
Gorilla = 48
Maize = 20
Potato = 48
Lion = 38
Monkey = 54
Tiger = 38
Dog = 78
Domestic Cat = 38
Chicken = 78
Mouse = 40
Crayfish = 200
Note:- Some insects are more than 1000.
Biochemistry and BSc biochemistry | Fundamentals of biochemistry