The rate of reaction is different types of factors, In a homogeneous system, factors like temperature, pressure, concentration, composition, etc. affect the rate of reaction, whereas in a heterogeneous system, heat transfer and mass transfer also affect the rate of reaction.
(i) Nature of Reactant & Product.
(ii) Temperature of System.
(iii) Concentration of Reactant.
(iv) Pressure of a System.
(v) Nature of catalyst if present.
(vi) Surface area of reactant.
(vii) Effect of Radiation.
{tocify} $title={Table of Contents}
Factors for Affecting Reaction Rate
(i) Nature of Reactant & Product
The rate of reaction is affected by the nature of the reactants and products. It depends on the breaking and formation of bonds in the reaction.
2NO +O2 ⟶ 2NO2
In the reaction, new bonds are formed by breaking the bonds of NO.
(ii) Temperature of System
The rate of reaction increases with an increase in temperature. For exothermic reactions, the rate of reaction decreases. Where for endothermic reactions the reaction speed increases.
(iii) Concentration of Reactant
As the concentration of reactant increases, the rate of reaction also increases accordingly.
Concentration (A) = No. of mole/Volume
In the above equation, if the concentration of A is doubled then the rate of reaction will also be doubled. By increasing the concentration of the reaction, the number of particles in the given volume will also increase, due to which the collision rate of molecules will increase, as a result, the rate of reaction will increase.
(iv) Pressure of a System
If the pressure is increased at a certain volume and temperature, the rate of reaction increases.
(v) Nature of Catalyst if Present
The rate of reaction is affected by the presence of a catalyst in the reaction.
(vi) Surface Area of the Reaction
In the case of heterogeneous reactions, the rate of reaction is proportional to the contact area between the phases. If the size of the reaction particles decreases, the surface area increases. Therefore the rate of reaction also depends on the size of the particle.
(vii) Effect of Radiation
Photo absorption of certain radiation increases the rate of certain reactions. This type of reaction are called photochemical reaction.
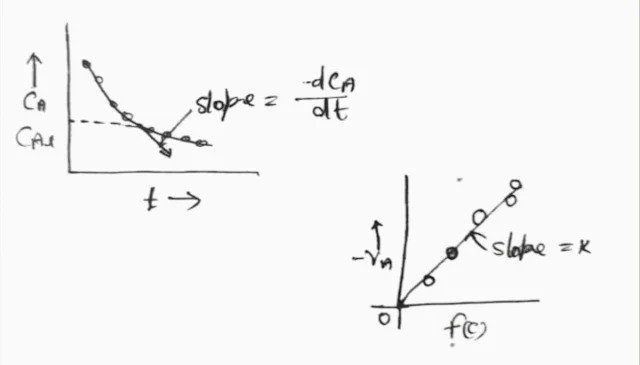
Differential Method of Analysis Data
This method deals directly with the rate equation. Procedure for analysis of the complete rate equation by differential method.
1. Suppose there is a rate equation, the rate equation can be written as follows.
-r_A = (-dC_A)/dt
2. To draw a graph plot of concentration v/s time from the collected data.
3. Draw a smooth curve using this data.
4. To determine the slope on this curve by drawing tangents from the curve per suitable concentration values.
5. Evaluate f(c) for each of the selected concentrations.
6. Plot a graph of (-dC_A)/ (dt).
7. If the curve is obtained from a straight line then the rate equation taken is correct. If straight lines are not obtained then the value of the rate equation is changed and another rate equation is tested.
Difference Between Elementry Reaction and Non-Elementry Reaction